Temsirolimus Glioblastoma : The Current State Of Potential Therapeutic Modalities For Glioblastoma Multiforme A Clinical Review Bentham Science
Methods Recurrent GBM patients with 1 chemotherapy regimen for progressive disease were eligible. A Study of Temsirolimus and Bevacizumab in Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators.

Pdf Phase I Ii Study Of Sorafenib In Combination With Temsirolimus For Recurrent Glioblastoma Or Gliosarcoma North American Brain Tumor Consortium Study 05 02
Half of patients with this diagnosis survive for less than 15 months.

Temsirolimus glioblastoma. To evaluate the effect of temsirolimus among patients with glioblastoma researchers treated 65 patients with glioblastoma with 250 mg of temsirolimus per week. Sorafenib and temsirolimus demonstrated limited activity with high rates of toxicity among patients with recurrent glioblastoma according to a. The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators.
Therefore we initiated a phase I trial of combined therapy in recurrent MGs to determine safety and a recommended phase II. The mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus and the AKT inhibitor perifosine are each well-tolerated as single agents but with limited activity reclinical data demonstrate synergistic anti-tumor effects from combined treatment. Document the activity profile of temsirolimus by the evaluation of overall survival at 1 year in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme without methylation of the MGMT gene promoter treated with temsirolimus before and concomitantly with radiotherapy followed by temsirolimus maintenance therapy.
Temsirolimus was administered in a 250-mg intravenous dose weekly. Temsirolimus was administered in a 250-mg intravenous dose weekly. Patients with MGMT unmethylated glioblastoma n 111 were randomized 11 between.
The mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus and the AKT inhibitor perifosine are each welltolerated as single agents but with limited activity reclinical data demonstrate synergistic antitumor effects from combined treatment. Patients n 257 fulfilling eligibility criteria underwent central MGMT testing. In recent years temsirolimus has been evaluated in clinical studies as a suggested treatment for GBM.
Background Temsirolimus CCI-779 is a small-molecule inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin mTOR and represents a rational therapeutic target against glioblastoma multiforme GBM. Glioblastoma multiforme is the most common type of brain tumor in adults. EORTC 26082 assessed the activity of temsirolimus in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma harboring an unmethylated O6 methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase MGMT promoter.
To define the safety profile of temsirolimus and sorafenib in non-EIAC patients. Mitogen-activated protein kinase MAPK activation and mammalian target of rapamycin mTOR-dependent signaling are hallmarks of glioblastoma. The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators.
Glioblastoma multiforme GBM is the most frequent aggressive and incurable central nervous system CNS tumorDespite conventional treatments such as surgery radiotherapy and chemotherapy there is no definite treatment for this disease. In the current study the authors conducted a phase 12 study of sorafenib an inhibitor of Raf kinase and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 VEGFR-2 and the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Temsirolimus CCI-779 is a small-molecule inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin mTOR and represents a rational therapeutic target against glioblastoma multiforme GBM.
Secondary Objectives - Phase I closed to accrual as of 01112008. To explore efficacy further we also evaluated the five bevacizumabnaive subjects with GBM who were treated at or above the MTD level 5 temsirolimus 115 mg weekly and perifosine 600mg on day 1 then 100 mg daily thereafter. The combination of temsirolimus and antibodies to vascular endothelial factor VEGF has not yet been investigated but with the hypothesis that temsirolimus might provide complimentary therapeutic benefit in combination with bevacizumab we included patients with progressive GBM after bevacizumab in an open phase II study.
The North American Brain Tumor Consortium examined the safety pharmacokinetics and efficacy of combination therapy with sorafenib a small molecule inhibitor of Raf vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 and platelet-derived growth factor receptorβ and temsirolimus CCI-779. Signaling though the PI3KAKTmTOR axis is activated in most MGs and therefore a potential therapeutic target. To assess the efficacy of temsirolimus and sorafenib in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma in non-EIAC patients as measured by progression-free survival status at six months PFS6.
Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the US. National Institutes of Health. Among these five there.
Sorafenib Combined With Erlotinib Tipifarnib or Temsirolimus in Treating Patients With Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme or Gliosarcoma. Methods Recurrent GBM patients with 1 chemotherapy regimen for progressive disease were eli-gible. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the US.
Malignant glioma MG is the most deadly primary brain cancer. The activity of single-agent targeted molecular therapies in glioblastoma has been limited to date. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the US.
Temsirolimus Temozolomide and Radiation Therapy in Treating Patients With Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma Multiforme.

Pdf Clinical Experiences With Temsirolimus In Glioblastoma Multiforme Is It Promising A Review Of Literature Semantic Scholar

Phase Ii Trial Of Temsirolimus In Children With High Grade Glioma Neuroblastoma And Rhabdomyosarcoma European Journal Of Cancer

Pediatric Patients With Refractory Central Nervous System Tumors Experiences Of A Clinical Trial Combining Bevacizumab And Temsirolimus Anticancer Research

Temsirolimus Promising For Treatment Of Breast Cancer Mantle Cell Lymphoma Cancerconnect

Combination Of Temsirolimus Cci 779 With Chemoradiation In Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma Multiforme Gbm Ncctg Trial N027d Is Associated With Increased Infectious Risks Clinical Cancer Research

Glioblastoma Targeted Therapy Updated Approaches From Recent Biological Insights Annals Of Oncology

Pdf Clinical Experiences With Temsirolimus In Glioblastoma Multiforme Is It Promising A Review Of Literature

Inhibitors Used In Glioblastoma Therapy Download Scientific Diagram

Current Trends In Glioblastoma Treatment Intechopen

Sorafenib Plus Temsirolimus Demonstrates Limited Benefit In Glioblastoma Cancer Therapy Advisor

The Current State Of Potential Therapeutic Modalities For Glioblastoma Multiforme A Clinical Review Bentham Science
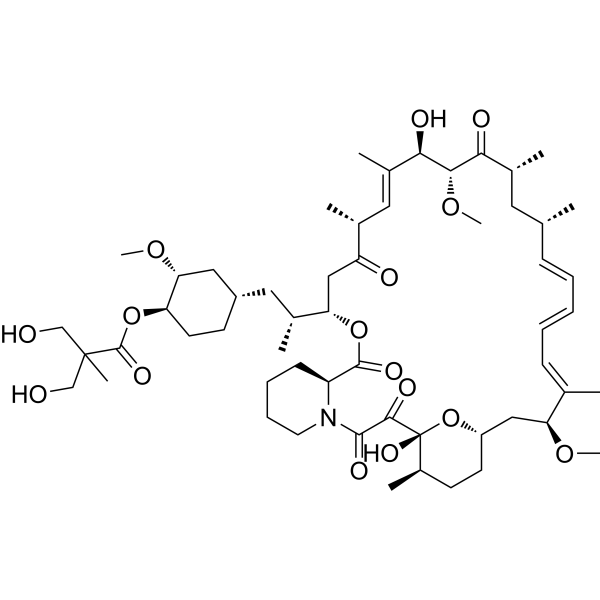
Temsirolimus Cci 779 Mtor Inhibitor Medchemexpress
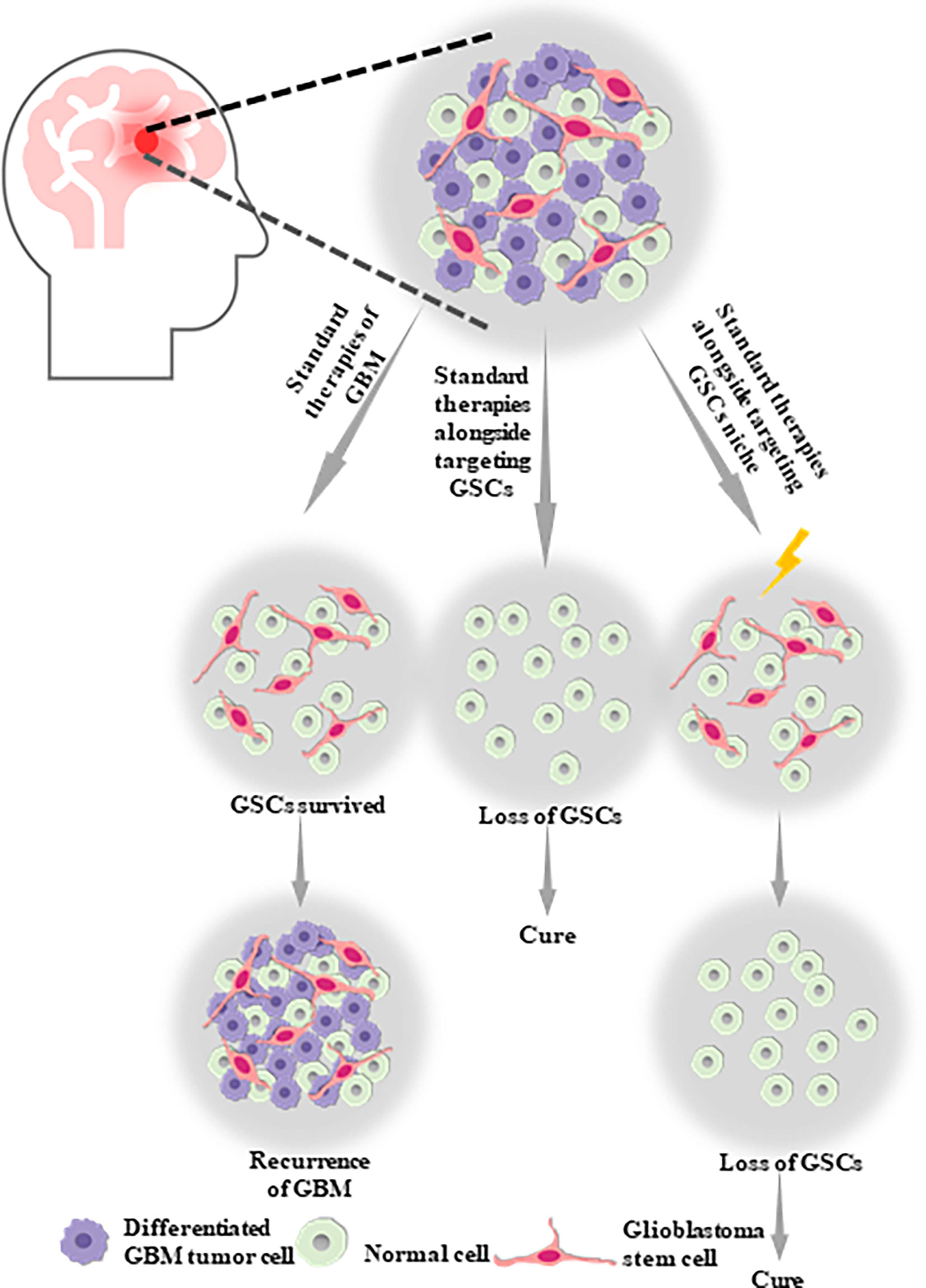
Frontiers Targeting Glioblastoma Stem Cells A Review On Biomarkers Signal Pathways And Targeted Therapy Oncology
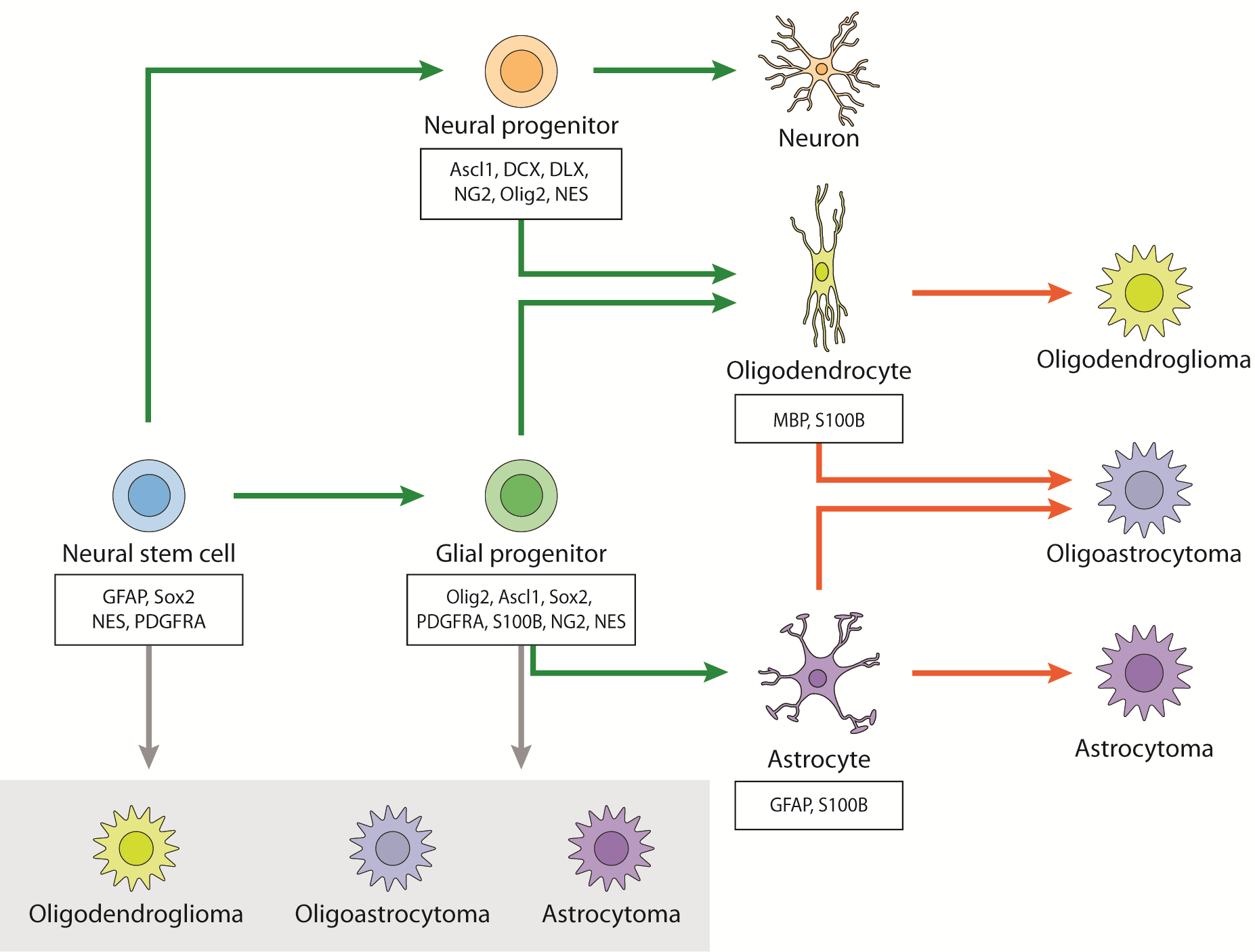
Mechanisms Of Aggressiveness In Glioblastoma Prognostic And Potential Therapeutic Insights Intechopen
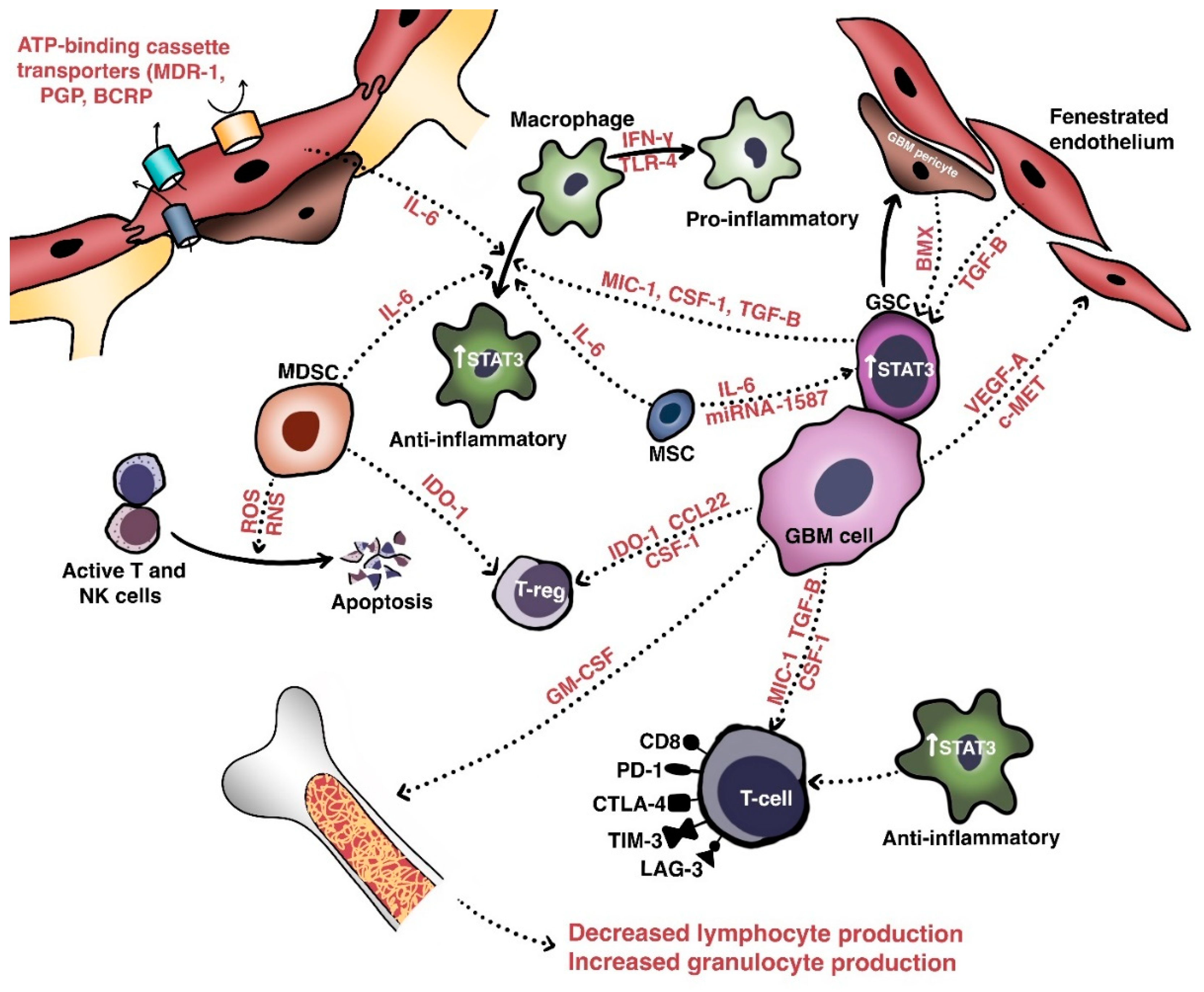
Ijms Free Full Text Molecular Mechanisms Of Treatment Resistance In Glioblastoma Html
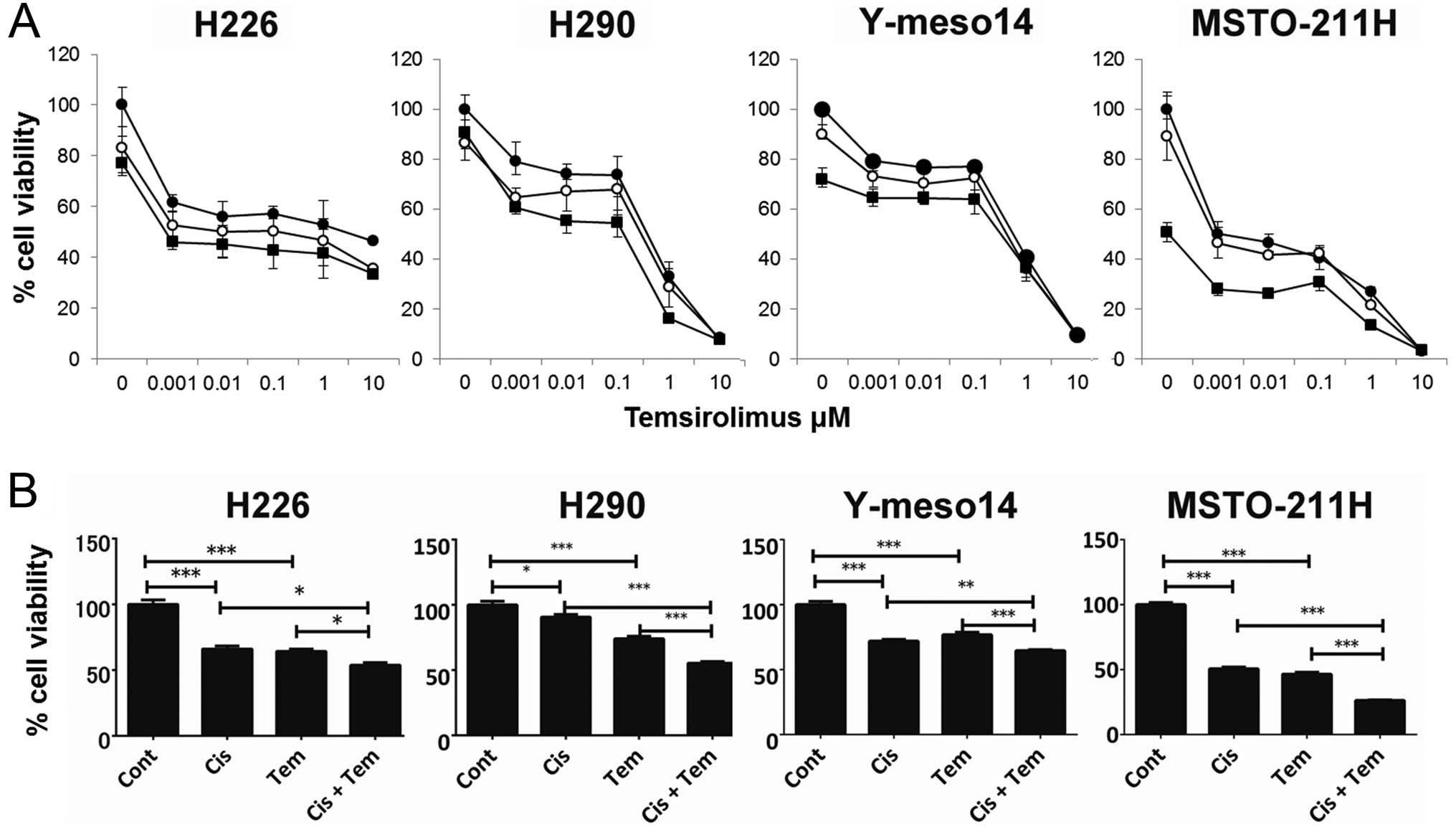
Antitumor Effect And Antiangiogenic Potential Of The Mtor Inhibitor Temsirolimus Against Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma

Pdf Clinical Experiences With Temsirolimus In Glioblastoma Multiforme Is It Promising A Review Of Literature Semantic Scholar

Thz1 And Temsirolimus Have A Synergistic Therapeutic Effect In A Mouse Download Scientific Diagram